First Class Tips About How To Detect Hip Dysplasia

However, adolescents and adults may also experience symptoms.
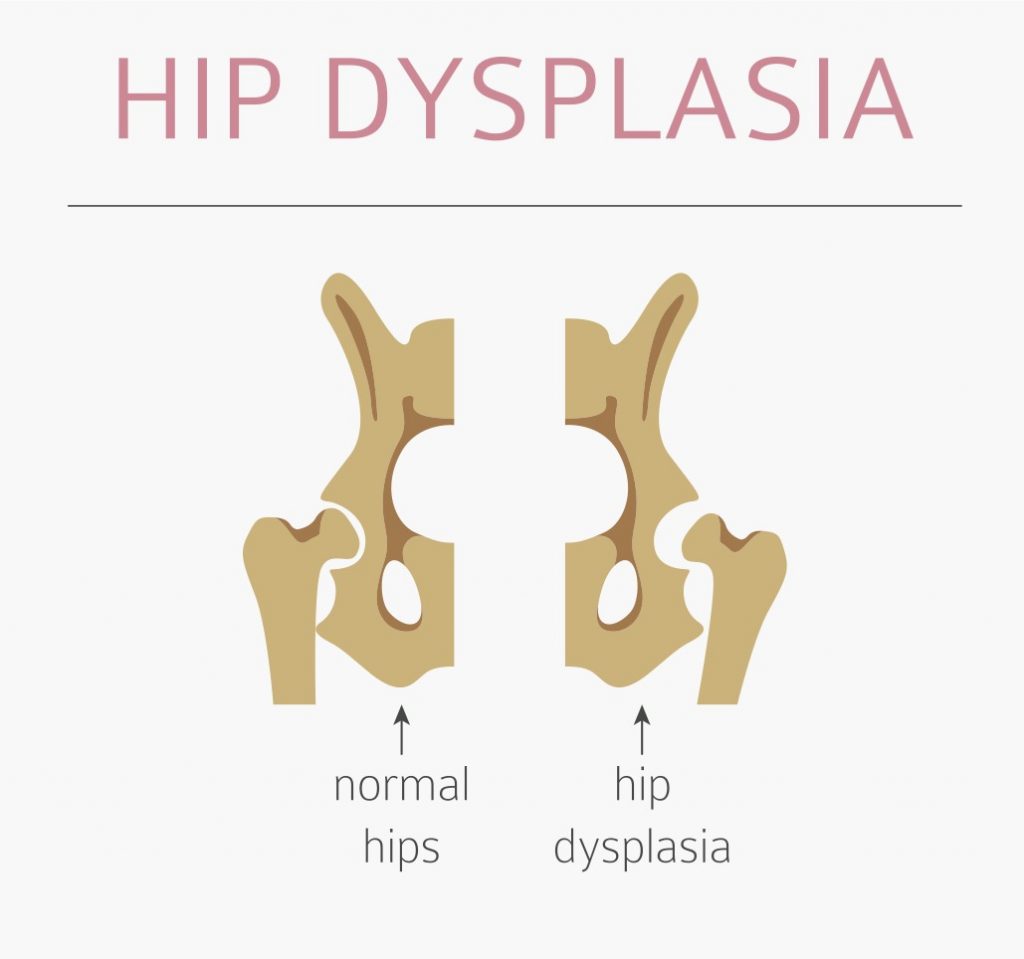
How to detect hip dysplasia. In a normal hip, the ball at the upper end of the thighbone fits firmly into the hip socket. A strong and dense fibrous sac that surrounds the hip joint muscles: We then develop a treatment plan to address your pain,.
[1] it is most often the. If the hip feels unstable or there is a history of hip problems in the family, your consultant may recommend imaging tests such as an ultrasound scan. Hip dysplasia prevents the hip joint from working properly and the joint wears out much faster than normal, much like a car’s tires will wear our faster when out of alignment.
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (ddh) describes a spectrum of conditions related to the development of the hip in infants and young children. Method 1 part 1: In a normal hip joint, the top (head) of the thighbone (femur) fits snugly into the hip socket.
Tell your provider when you first noticed hip pain and if any activity. It is more common in girls than boys. Physical examination findings such as limited hip abduction (lha), asymmetric skin creases (asc), and a popping sensation in the hip facilitate the.
In a child with ddh, the hip socket is shallow. Mild cases of hip dysplasia can be difficult to diagnose and might not start causing problems until you're a young adult. Hip dysplasia can occur when a baby’s hip joint does not develop properly.
Departments care at mayo clinic overview hip dysplasia is the medical term for a hip socket that doesn't fully cover the ball portion of the upper thighbone. Recognizing the signs in young dogs download article 1 pay attention to the shape of your dog’s back.
A healthcare provider will move the hip joint in different directions to see which movements. Contacting a doctor outlook summary hip dysplasia occurs when the two bones that come together in the hip joint — the pelvis and femur bones — are out of. It is usually detected in babies.
It is the preferred way to diagnose hip dysplasia in babies up to 6 months of age. A healthcare provider will diagnose hip dysplasia with a physical exam and some imaging tests. Diagnosing ddh your baby's hips will be checked as part of the newborn physical screening examination within 72 hours of being born, and again at 6 to 8 weeks of age.
Strong muscles surround the hip joint, and need to work in the correct. Ideally, ddh is detected by routine history and physical exam in the neonatal period. Stocksy hip dysplasia is a fairly common condition in babies that can happen from improper uses of a swaddle or baby carrier.
Diagnosing hip dysplasia in adolescents also involves a physical exam. Mild cases of hip dysplasia. Questions to the parents regarding risk factors can be important.